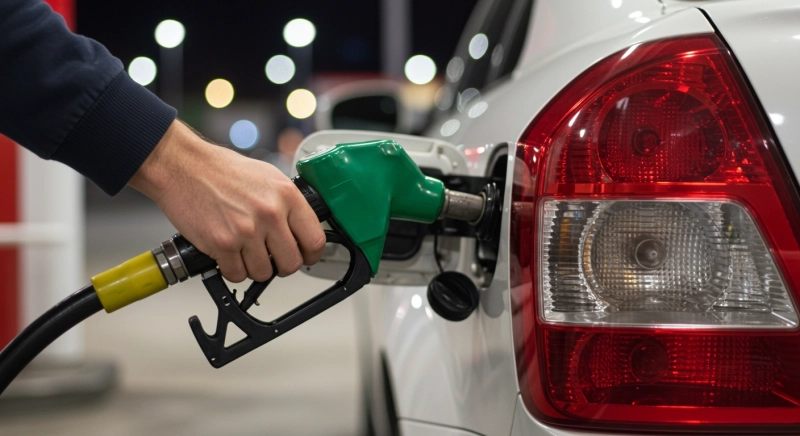
Today, owning a car directly impacts the quality of life positively. Of course, there are certain costs associated with owning a car and various advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of fuel your chosen car uses. In this article, while exploring the advantages and disadvantages of diesel and gasoline vehicles, we will examine both types in depth.
Gasoline Vehicles
Gasoline vehicles operate on the energy produced from the reaction of gasoline and oxygen. This energy creates pressure, which causes the engine pistons to move.
Advantages of Gasoline Vehicles
1. Affordability: Gasoline vehicles are generally more affordable to purchase compared to diesel vehicles because their fuel costs are higher. Hence, the most noticeable advantage in comparing the two types is that gasoline vehicles are cheaper.
2. Ease of Operation: Gasoline vehicles operate more smoothly since the fuel reacts faster, leading to quieter performance.
4. Maintenance Intervals and Costs: Gasoline vehicles usually have more favorable maintenance intervals and costs compared to diesel vehicles. While diesel vehicles typically require servicing every 10,000 kilometers, gasoline vehicles usually need service between 15,000 and 20,000 kilometers. This variation depends on the manufacturer and specific vehicle model.
4. Performance: Due to their quicker-reacting fuel, gasoline vehicles generally offer better performance compared to diesel vehicles.
5. LPG Compatibility: Given the rising fuel prices, gasoline engines can be adapted to run on LPG gas through various modifications, making them more advantageous than diesel vehicles.
Disadvantages of Gasoline Vehicles
- Higher Fuel Costs: The most apparent disadvantage of gasoline vehicles is the higher cost of gasoline per liter, and gasoline engines generally consume more fuel. This makes fuel consumption a significant cost factor in vehicle ownership.
Diesel Vehicles
While exploring the advantages and disadvantages of diesel and gasoline vehicles, it is also important to understand the differences in their operating principles. Diesel engines do not require components like spark plugs or carburetors. Instead, the air in the combustion chamber is compressed by the cylinder and heated to nearly 500 degrees Celsius, with fuel sprayed on the heated air to create explosions. This results in significantly higher power output compared to gasoline engines, making diesel engines preferred for load-carrying vehicles.
Advantages of Diesel Vehicles
1. Fuel Efficiency: Diesel is less volatile than gasoline, leading to longer combustion processes and better fuel efficiency, offering more kilometers per liter. The cost savings are even greater given the typically lower price of diesel fuel per liter.
2. Torque: Diesel engines produce more torque due to their operating principles and design, enabling them to perform effectively under heavy loads.
3. Resale Value: Diesel vehicles generally find buyers more easily and at higher prices when sold. Their advantages and suitability for specific uses contribute to their faster resale.
Disadvantages of Diesel Vehicles
1. Higher Maintenance Costs: Diesel vehicles have higher maintenance costs due to their different operating principles and design compared to gasoline vehicles.
2. Higher Purchase Cost: Diesel vehicles are generally more expensive to purchase compared to gasoline vehicles.
3. Increased Likelihood of Malfunctions: Diesel vehicles are more prone to malfunctions due to their fuel type and operational mechanics.
4. Noise: Diesel engines produce high torque, which makes them noisier. If you are sensitive to noise, it's advisable to listen to the vehicle's sound before purchasing a diesel vehicle.
5. LPG Modification: Unlike gasoline vehicles, diesel vehicles cannot be modified to run on LPG.
In this article, we aimed to address the advantages and disadvantages of diesel and gasoline vehicles and discussed the operating principles of engines using both fuel types. If you are involved in the car rental business, you can benefit from Titarus services to manage all operations, including fuel types, maintenance schedules, and similar processes for rental vehicles.